二叉树
二叉树
二叉树
- binary tree, 每个节点最多只有两个分支
- 完全二叉树, Complete Binary Tree, 在一棵二叉树中,若除最后一层外的其余层都是满的,并且最后一层要么是满的,要么在右边缺少连续若干节点
- 最大堆, 最小堆
- 二叉搜索树, Binary Search Tree, 是指一棵空树或者具有下列性质的二叉树:
若任意节点的左子树不空,则左子树上所有节点的值均小于它的根节点的值;
若任意节点的右子树不空,则右子树上所有节点的值均大于它的根节点的值;
任意节点的左、右子树也分别为二叉搜索树. - 平衡二叉搜索树, Balanced Binary Search Tree, 是一种结构平衡的二叉搜索树,它是一种每个节点的左右两子树高度差都不超过1的二叉树。
- AVL树, Adelson-Velsky and Landis Tree
- 红黑树, red-black tree
- 多叉树
- B树 B-tree
- B+树 B+-tree
- B*树 B*-tree
算法
遍历
- 深度优先遍历 depth-first order
- 前序遍历, Preorder Traversal, 根左右
- 中序遍历, Inorder Traversal, 左根右
- 后序遍历, Postorder Traversal, 左右根
1 2 3 4 5 6
def Traversal(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]: if not root: return [] return [root.val] + self.Traversal(root.left) + self.Traversal(root.right) # preorder return self.Traversal(root.left) + [root.val] + self.Traversal(root.right) # inorder return self.Traversal(root.left) + self.Traversal(root.right) + [root.val] # postorder
- 广度优先遍历 breadth-first order 层序遍历, Level-Order Traversal, 从上到下,从左到右
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
def Traversal(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]: if not root: return [] queue = [root] res = [] while queue: node = queue.pop(0) res.append(node.val, 0) if node.left: queue.insert(0, node.left) if node.right: queue.insert(0, node.right) return res
查找
在遍历中直接查找
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
def Search(self, root: TreeNode, id: int, search_method: str ="preorder") -> TreeNode|None:
if not root:
return None
match search_method:
case "preorder":
return (root if root.val==id else None) or self.Search(root.left, id, search_method) or self.Search(root.right, id, search_method)
case "inorder":
return self.Search(root.left, id, search_method) or (root if root.val==id else None) or self.Search(root.right, id, search_method)
case "postorder":
return self.Search(root.left, id, search_method) or self.Search(root.right, id, search_method) or (root if root.val==id else None)
删除
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
def Delete(self, root: TreeNonde, id:int, parent: TreeNode=None) -> TreeNode|None:
if not root:
return None
if root.val == id:
return None
if root.left and root.left.val == id:
root.left = None
return root
elif root.right and root.right.val == id:
root.right = None
return root
return self.Delete(root.left, id, root) or self.Delete(root.right, id, root)
完全二叉树
如果是广度优先搜索的完全二叉树, 可以将二叉树以数列的方式存储, 数列的第 i 个元素为 i 节点的值, 其左子节点为 2i+1, 右子节点为 2i+2, 父节点为 (i-1)//2.
对于最小堆结构, python 库 heapq 提供了一个最小堆的实现, 可以直接使用.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
class MinHeap:
def __init__(self):
self.heap = []
def parent(self, i):
return (i - 1) // 2
def left_child(self, i):
return 2 * i + 1
def right_child(self, i):
return 2 * i + 2
def swap(self, i, j):
self.heap[i], self.heap[j] = self.heap[j], self.heap[i]
def heapify_up(self, i):
"""从节点 i 向上调整,维持堆结构"""
while i > 0 and self.heap[i] < self.heap[self.parent(i)]:
self.swap(i, self.parent(i))
i = self.parent(i)
def heapify_down(self, i):
"""非递归方式向下调整堆"""
n = len(self.heap)
while True:
smallest = i
left = self.left_child(i)
right = self.right_child(i)
if left < n and self.heap[left] < self.heap[smallest]:
smallest = left
if right < n and self.heap[right] < self.heap[smallest]:
smallest = right
if smallest == i:
break # 当前节点已经比子节点小,无需继续调整
self.swap(i, smallest)
i = smallest # 继续向下调整
def insert(self, val):
"""插入元素"""
self.heap.append(val)
self.heapify_up(len(self.heap) - 1)
def extract_min(self):
"""删除并返回堆顶元素(最小值)"""
if not self.heap:
return None
min_val = self.heap[0]
last_val = self.heap.pop()
if self.heap:
self.heap[0] = last_val
self.heapify_down(0)
return min_val
def build_heap(self, arr):
"""从数组构建堆(原地堆化)"""
self.heap = arr
n = len(arr)
# 从最后一个非叶子节点开始调整
for i in range(n // 2 - 1, -1, -1):
self.heapify_down(i)
取一个数列的前 k 个最大值: 维护一个大小为 k 的最小堆.
AVL树
查找、插入和删除在平均和最坏情况下的时间复杂度都是 $O(\log n)$.
节点的平衡因子是它的左子树的高度减去它的右子树的高度
参考1, 参考2
左旋与右旋:
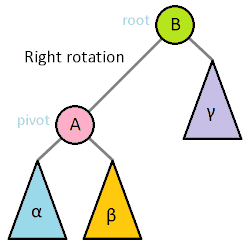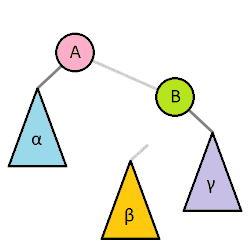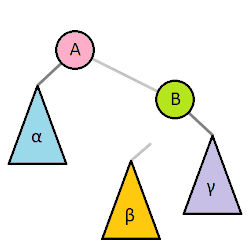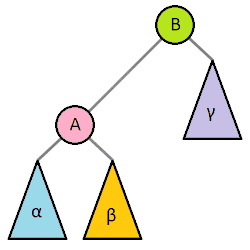
插入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
def Insert(self, root: TreeNode, id: int) -> TreeNode:
if not root:
return TreeNode(val=id, balance=0, parent=None)
# 1. 二叉搜索树的插入
parent = None
current = root
while current:
if id < current.val:
parent = current
current = current.left
elif id > current.val:
parent = current
current = current.right
else:
return None
current = TreeNode(val=id, balance=0, parent=parent)
if id < parent.val:
parent.left = current
else:
parent.right = current
# 2. 从插入点向上回溯,更新平衡因子
while(parent):
if parent.left == current:
parent.balance += 1
else:
parent.balance -= 1
if parent.balance == 0:
break
elif parent.balance == 1 or parent.balance == -1:
current = parent
parent = parent.parent
else:
# 3. 从第一个平衡因子绝对值大于1的节点开始,向下旋转,使其平衡
if parent.balance == 2:
if current.balance == 1:
# LL型,右旋, balance(current, parent)=(1, 2)->(0, 0)
self.RightRotate(parent)
else:
# LR型,先左旋再右旋
self.LeftRotate(current)
self.RightRotate(parent)
parent.balance = -1
else:
if current.balance == -1:
# RR型,左旋
self.LeftRotate(parent)
else:
# RL型,先右旋再左旋
self.RightRotate(current)
self.LeftRotate(parent)
parent.balance = 1
break
def RightRotate(self, node: TreeNode):
parent = node.parent
left = node.left
right = left.right
if parent:
if parent.left == node:
parent.left = left
else:
parent.right = left
else:
self.root = left
left.parent = parent
left.right = node
node.parent = left
node.left = right
if right:
right.parent = node
node.balance = 0
left.balance = 0
def LeftRotate(self, node: TreeNode):
parent = node.parent
right = node.right
left = right.left
if parent:
if parent.left == node:
parent.left = right
else:
parent.right = right
else:
self.root = right
right.parent = parent
right.left = node
node.parent = right
node.right = left
if left:
left.parent = node
node.balance = 0
right.balance = 0
flowchart LR;
subgraph LL型
direction TB
a1([a:2])-->b1([b:1]); a1-->c1["c(h)"];
b1-->d1[["d(h+1)"]]; b1-->e1["e(h)"];
end
subgraph 旋转
direction TB
b2([b:0])-->d2[["d(h+1)"]]; b2-->a2([a:0]);
a2-->e2["e(h)"]; a2-->c2["c(h)"];
end
LL型-->|右旋|旋转
flowchart LR;
subgraph RR型
direction TB
a1([a:-2])-->b1["b(h)"]; a1-->c1([c:-1]);
c1-->d1["d(h)"]; c1-->e1[["e(h+1)"]];
end
subgraph 旋转
direction TB
c2([c:0])-->a2([a:0]); c2-->e2[["e(h+1)"]];
a2-->b2["b(h)"]; a2-->d2["d(h)"];
end
RR型-->|左旋|旋转
flowchart LR;
subgraph LR型
direction TB
a1([a:2])-->b1([b:-1]); a1-->c1["c(h+1)"];
b1-->d1["d(h+1)"]; b1-->e1([e:1]);
e1-->f1[["f(h+1)"]]; e1-->g1["g(h)"];
end
subgraph 旋转1
direction TB
a2([a:2])-->e2([e:2]); a2-->c2["c(h+1)"];
e2-->b2([b:0]); e2-->g2["g(h)"];
b2-->d2["d(h+1)"]; b2-->f2[["f(h+1)"]];
end
subgraph 旋转2
direction TB
e3([e:0])-->b3([b:0]); e3-->a3([a:-1]);
b3-->d3["d(h+1)"]; b3-->f3[["f(h+1)"]];
a3-->g3["g(h)"]; a3-->c3["c(h+1)"];
end
LR型-->|左旋|旋转1-->|右旋|旋转2
flowchart LR;
subgraph RL型
direction TB
a1([a:-2])-->b1["b(h+1)"]; a1-->c1([c:1]);
c1-->d1([d:-1]); c1-->e1["e(h+1)"];
d1-->f1["f(h)"]; d1-->g1[["g(h+1)"]];
end
subgraph 旋转1
direction TB
a2([a:-2])-->b2["b(h+1)"]; a2-->d2([d:-2]);
d2-->f2["f(h)"]; d2-->c2([c:0]);
c2-->g2[["g(h+1)"]]; c2-->e2["e(h+1)"];
end
subgraph 旋转2
direction TB
d3([d:0])-->a3([a:1]); d3-->c3([c:0]);
a3-->b3["b(h+1)"]; a3-->f3["f(h)"];
c3-->g3[["g(h+1)"]]; c3-->e3["e(h+1)"];
end
RL型-->|右旋|旋转1-->|左旋|旋转2
删除
B树
参考
B树(B-tree),是一种自平衡的树,能够保持数据有序。这种数据结构能够让查找数据、顺序访问、插入数据及删除的动作,都在对数时间内完成。B树,概括来说是一个一般化的二叉搜索树(binary search tree), 一个节点可以拥有2个以上的子节点。
一个 $t$ 度($2t$ 阶)的B树是一个有以下属性的树:(参考)
- 每个非根节点至少有 $t-1$ 个键, 根节点至少有一个键
- 每个节点至多有 $2t-1$ 个键
- 如果一个非叶节点有 $k$ 个键,那么它必然有 $k+1$ 个子节点
- 每个节点的键都按照升序排列, 两键之间的子节点的键值位于这两键之间
flowchart TB;
a[100]---b1[35 65]; a---b2[130 180]
b1---c1[10 20]; b1---c2[40 50]; b1---c3[70 80 90]
b2---d1[110 120]; b2---d2[140 160]; b2---d3[190 240 260]
插入
aggressive splitting 参考
所有的插入都从根节点开始。当要访问子节点发现子节点已满时, 即将它分裂.
- 从根节点开始, 向下遍历
- 当前节点 $x$ 为根节点时, 查看根节点 $x$
- 若节点已满, 创建一个新的根节点, 将 $x$ 作为新根节点的子节点, 分裂该节点 $x$, 并移动到 $x$ 的子节点
- 当前节点 $x$ 为非叶节点时, 查看要移动的下一个节点 $y$
- 若要查看的节点未满, 移动到该节点 $y$
- 若要查看的节点已满, 分裂该节点 $y$, 并移动到 $y$ 的子节点
- 循环步骤2, 直到当前节点为叶节点, 插入新的键
分裂:
- 从当前节点的键中选出中位数作为键, 小于这一中位数的元素放入左节点, 大于这一中位数的元素放入右节点
- 将新二叉树的键按顺序插入父节点的键中, 新二叉树的左右节点按顺序插入父节点的子节点中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
class BTreeNode:
def __init__(self, t: int, leaf:boolean):
self.t = t # B树的度, 允许的键数[t-1, 2t-1]
self.leaf = leaf # True为叶节点
self.keys = [None] * (2 * t - 1)
self.children = [None] * (2 * t) # 子节点
self.n = 0 # 键数
def insert_non_full(self, key: int):
# 不管是否为叶节点, self的键都没有填满
i = self.n - 1
if self.leaf:
while i >= 0 and key < self.keys[i]:
self.keys[i + 1] = self.keys[i]
i -= 1
self.keys[i + 1] = key
self.n += 1
else:
while i >= 0 and key < self.keys[i]:
i -= 1
if self.children[i + 1].n == 2 * self.t - 1:
self.split_child(i + 1, self.children[i + 1])
if key > self.keys[i + 1]:
i += 1
self.children[i + 1].insert_non_full(key)
def split_child(self, i: int, child: BTreeNode):
# 分裂self的第i个子节点child
# 原本的child分为t-1(child), key(插入self), t-1(new_node)
new_node = BTreeNode(self.t, child.leaf) # 右节点
new_node.keys = child.keys[self.t:]
new_node.n = self.t - 1
child.keys = child.keys[:self.t - 1]
child.n = self.t - 1
if not child.leaf:
new_node.children = child.children[self.t:]
child.children = child.children[:self.t]
self.keys.insert(i, child.keys[self.t - 1])
self.children.insert(i + 1, new_node)
self.n += 1
class BTree:
def __init__(self, t: int):
self.t = t
self.root = None
def insert(self, key: int): # 插入的主函数
if self.root is None: # 没有root节点
self.root = BTreeNode(self.t, True)
self.root.keys[0] = key
self.root.n = 1
return
if self.root.n == 2 * self.t - 1: # root节点已满
new_node = BTreeNode(self.t, False)
new_node.children[0] = self.root
new_node.split_child(0, self.root)
new_node.insert_non_full(key)
self.root = new_node
else:
self.root.insert_non_full(key)
删除
搜索要删除的元素, 如果它在
- 叶子节点
- 将它从中删除
- 如果发生了下溢出,从该节点删除后重新平衡重新调整树
- 否则, 在非叶节点
- 选择一个新的分隔符(左子树中最大的元素或右子树中最小的元素),将它从叶子节点中移除,替换掉被删除的元素作为新的分隔值
- 对于这个叶节点, 如果发生了下溢出,从该节点删除后重新平衡重新调整树
删除后重新平衡: (参考左旋与右旋)
- 如果缺少元素节点的右兄弟存在且拥有多余的元素,那么向左旋转
- 否则,如果缺少元素节点的左兄弟存在且拥有多余的元素,那么向右旋转
- 否则,如果它的两个直接兄弟节点都只有最小数量的元素,那么将它与一个直接兄弟节点以及父节点中它们的分隔值合并
B+树
B*树
红黑树
参考
红黑树(Red–black tree)是一种自平衡二叉查找树,是在计算机科学中用到的一种数据结构,典型用途是实现关联数组。它在1972年由 Rudolf Bayer 发明,被称为“对称二叉B树”。红黑树的结构复杂,但它的操作有着良好的最坏情况运行时间,并且在实践中高效:它可以在 $ O(\log n)$ 时间内完成查找、插入和删除。
本文由作者按照 CC BY 4.0 进行授权